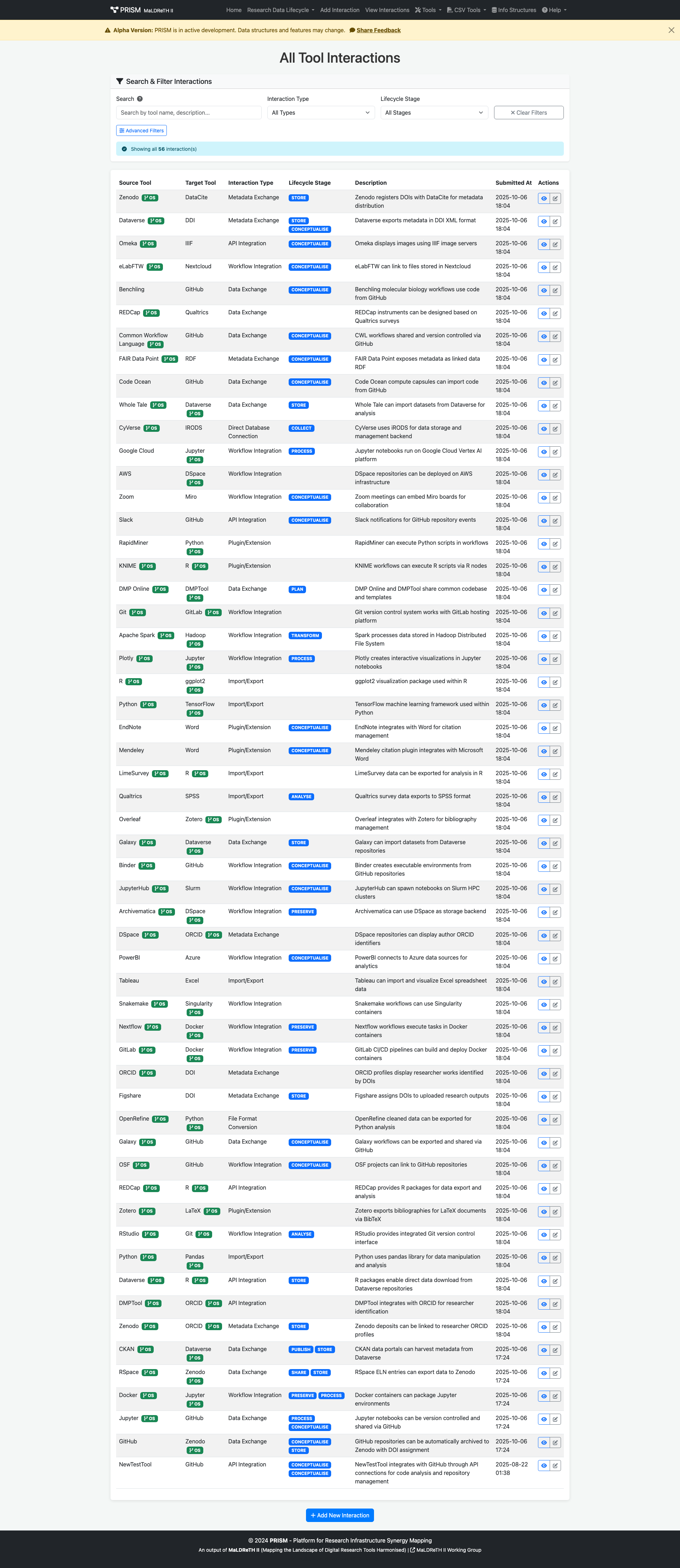
What is a Tool Interaction?
A tool interaction in PRISM represents a connection or integration between two research tools in the digital research ecosystem. Interactions enable data flow, functionality enhancement, or workflow integration across the research data lifecycle.
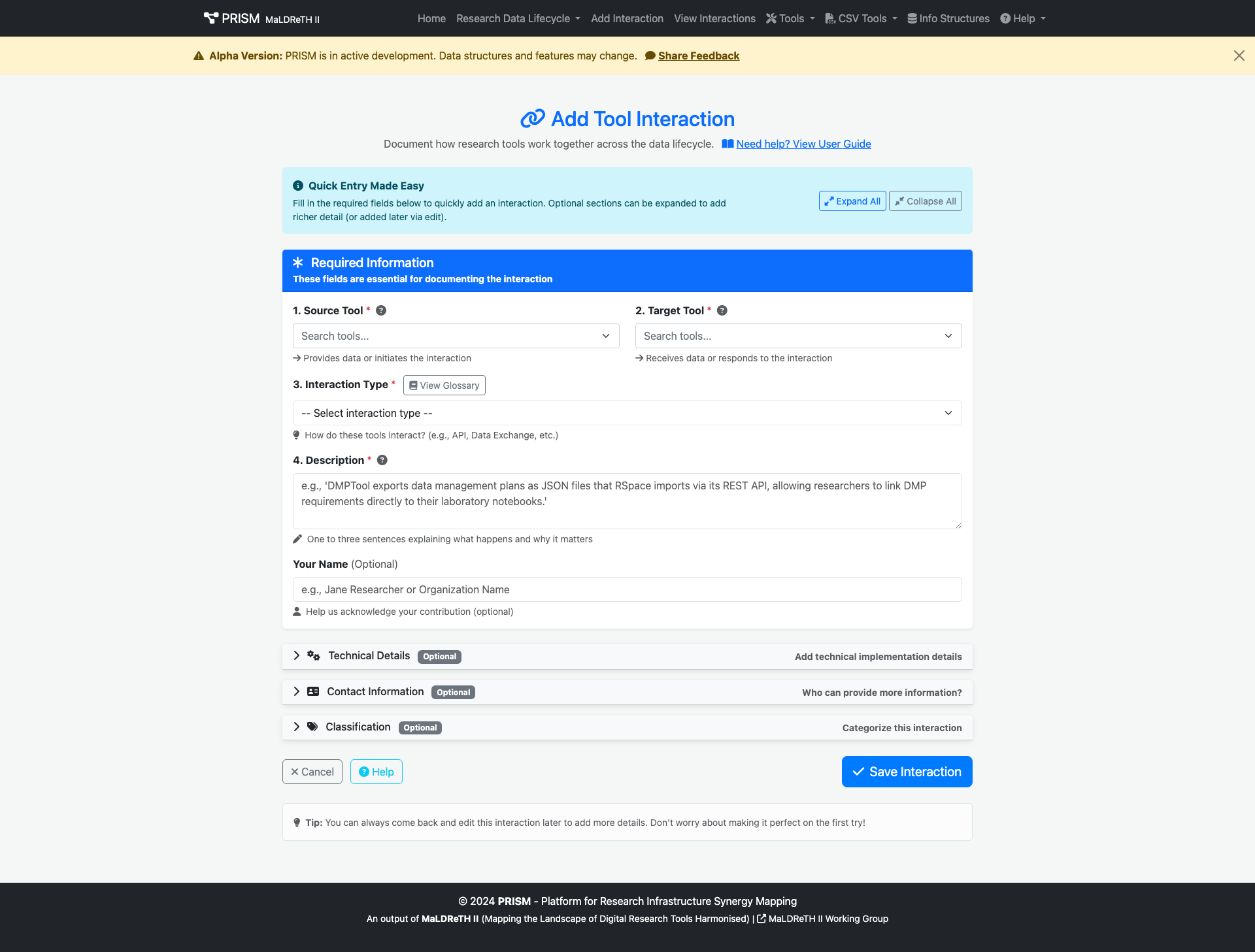
Source Tool
Initiates or provides data/functionality
Interaction Type
How the tools connect
Target Tool
Receives data/functionality
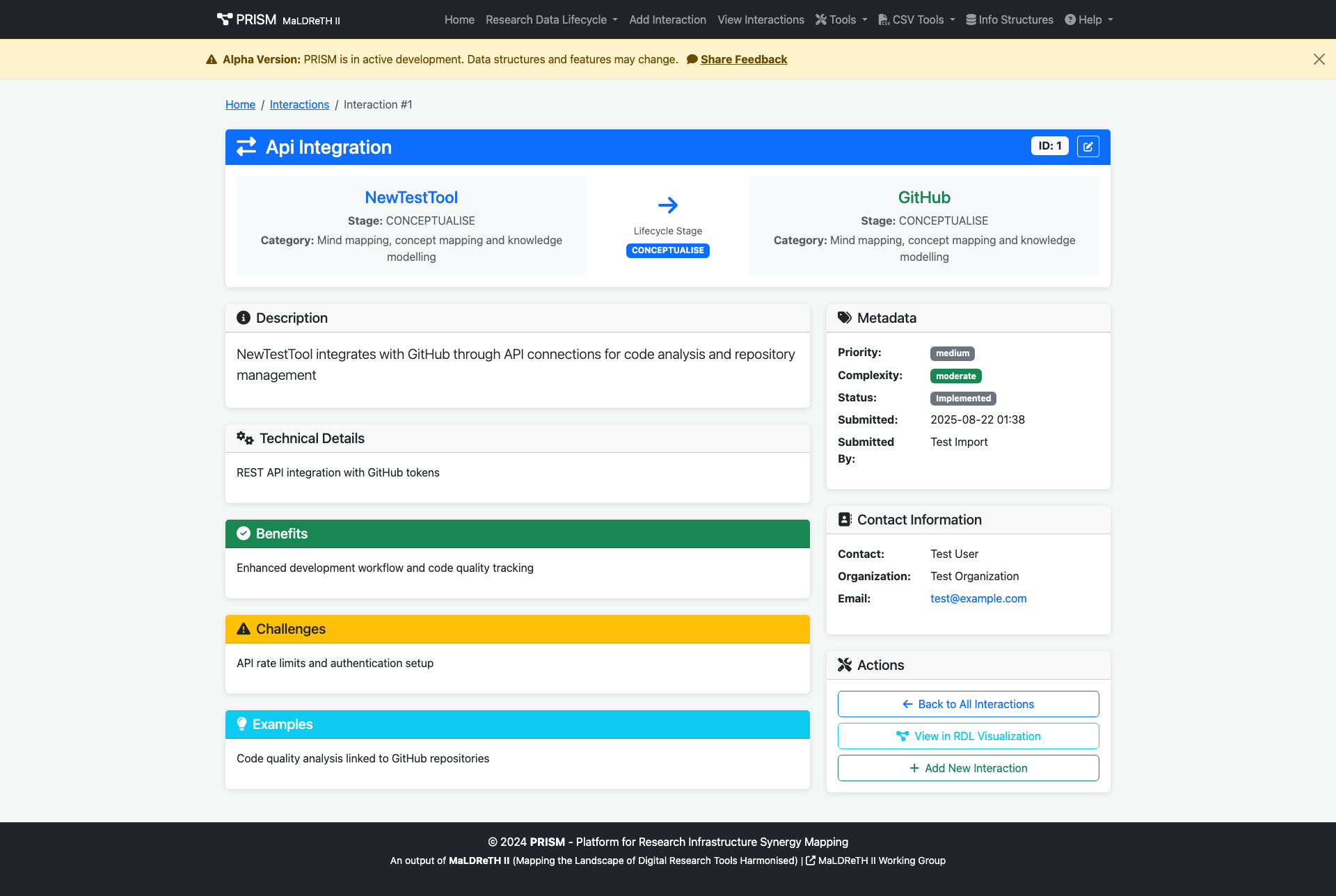
Example Interaction
GitHub Zenodo
- Type: Data Exchange
- Stage: PRESERVE
- Description: GitHub repositories are automatically archived to Zenodo with DOI assignment, creating permanent records of research software.
Components of an Interaction
Every interaction consists of essential elements:
- Source Tool - The tool that initiates the connection
- Target Tool - The tool that receives or responds
- Interaction Type - The mechanism of connection (API, data exchange, etc.)
- Description - What happens and why it matters
- Lifecycle Stages - Auto-computed from the source and target tools' assigned stages
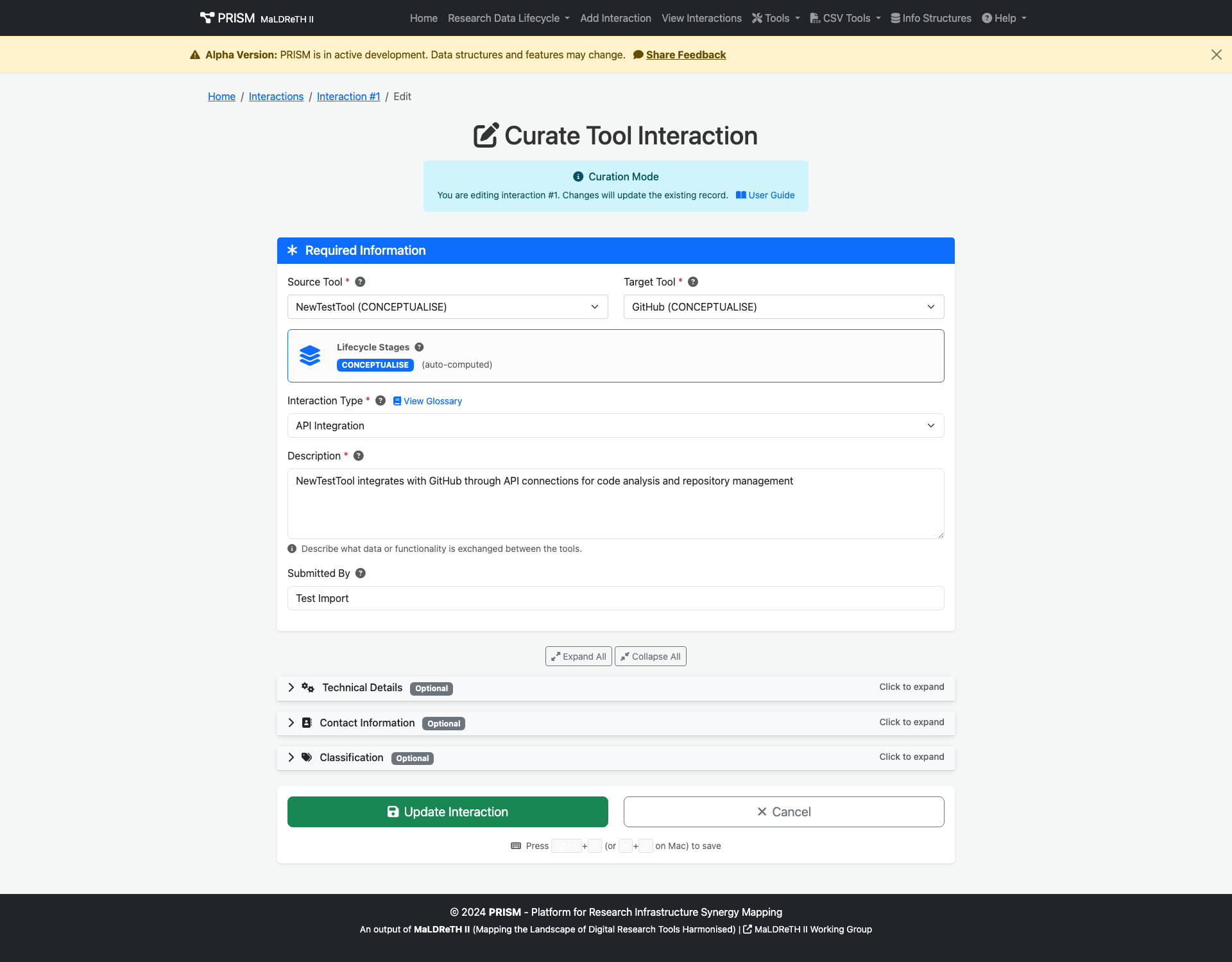
Automatic Lifecycle Stage Detection
As of November 2025, PRISM automatically determines lifecycle stages from the selected tools. When you choose your source and target tools, their lifecycle stages are displayed automatically—no manual selection needed!